Alberto Acerbi and Domenico Parisi (2006)
Cultural Transmission Between and Within Generations
Journal of Artificial Societies and Social Simulation
vol. 9, no. 1
<https://www.jasss.org/9/1/9.html>
For information about citing this article, click here
Received: 08-Jun-2005 Accepted: 21-Nov-2005 Published: 31-Jan-2006
 Abstract
Abstract
 |
| Figure 1. An agent's visual field and the input encoding the content of the visual field |

|
| Figure 2. Cultural transmission model |

|
| Figure 3. Average performance of a succession of 500 generations for a population with purely inter-generational transmission [average of 10 seeds] |

|
| Figure 4. Average performance of a succession of 500 generations for a population with purely intra-generational transmission [average of 10 seeds] |

|
| Figure 5. Comparison between the average performance of a succession of 500 generations for populations with inter-generational cultural transmission with noise (grey line) and without noise (black line) [average of 10 seeds] |

|
| Figure 6. Comparison between the average performance of a succession of 500 generations for populations with inter-generational cultural transmission without noise for learning rate = 0.1 (grey line) and for learning rate = 0.3 (black line) [average of 10 seeds] |
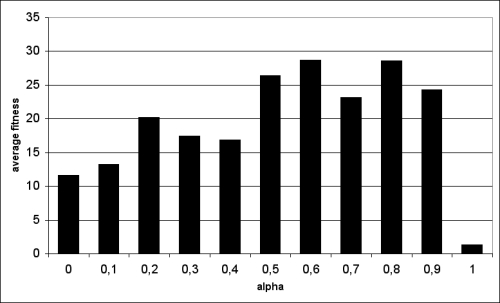
|
| Figure 7. Average performance in the last 100 generations as a function of level of (α= 0: purely inter-generational transmission; α = 1: purely intra-generational transmission ) [average of 10 seeds] |

|
| Figure 8. Comparison between the average performance of a succession of 500 generations for populations with cultural transmission without noise with α = 0.6 (i.e., a certain amount of horizontal transmission; grey line) and with α = 0 (purely inter-generational cultural transmission; black line) [average of 10 seeds] |

|
| Figure 9. Average performance of the last 100 generations as a function of level of α [average of 10 seeds] |

|
| Figure 10. Comparison between the average performance of a population with cultural transmission with α = 0.3 (grey line) and a population with α = 0, namely with pure inter-generational cultural transmission (black line), after the environment has changed [average of 10 seeds] |

|
| Figure 11. Value of the gene that controls the probability α that an individual will imitate its peers vs adults [average of 10 seeds] |

|
| Figure 12. Performance of a population with the α value controlled by a genetic algorithm [average of 10 seeds] |

|
| Figure 13. Comparison between the performance of a population with the probability α of intra-generational cultural transmission controlled by a genetic algorithm (grey line) and a population with α = 0, namely with pure inter-generational cultural transmission (black line), after the environment has changed [average of 10 seeds] |
BELEW, R.K. (1990) Evolution, learning, and culture: computational metaphors for adaptive search. Complex Systems 4(1): 11-49.
BORENSTEIN, E. AND RUPPIN, E. (2003) Enhancing autonomous agents evolution with learning by imitation. AISB Journal 1(4).
BOYD, R. AND RICHERSON P. J. (1985) Culture and the Evolutionary Process. Chicago: Chicago University Press.
CANGELOSI, A. AND PARISI, D. (1998) The emergence of a 'language' in an evolving population of neural networks. Connection Science, 10, 83-97.
CANGELOSI, A., GRECO, A. & HARNAD, S. (2000). From robotic toil to symbolic theft: Grounding transfer from entry-level to higher-level categories. Connection Science, 12(2), 143-162.
CAVALLI-SFORZA, L. L. AND FELDMAN M. (1981) Cultural Transmission and Evolution: a Quantitative Approach, Princeton: Princeton University Press.
CHATTOE, E. (1998) Just how (un)realistic are evolutionary algorithms as representations of social processes? Journal of Artificial Societies and Social Simulation 1(3), https://www.jasss.org/1/3/2.html.
DENARO, D. AND PARISI, D. (1996) "Cultural evolution in a population of neural networks". in Neural nets. Wirn-96. Edited by M. Marinaro, R. Tagliaferri. pp. 100 - 111. New York: Springer.
HUTCHINS, E. AND HAZLEHURST, B. (1995) "How to invent a lexicon: the development of shared symbols in interaction". in Artificial Societies: The computer simulation of social life. Edited by G. N. Gilbert and R. Conte. pp. 157-189. London: UCL Press.
HEWLETT, B. S. AND CAVALLI-SFORZA , L. L. (1986) Cultural transmission among Aka pygmies. American Anthropologist 88(4): 922 - 933.
KNAFO, A. AND SCHWARTZ, S. H. (2001) Value Socialization in Families of Israeli-Born and Soviet-Born Adolescents in Israel. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology 32(2): 213 - 228.
MCQUESTEN, P. AND MIIKKULAINEN, R. (1997) Culling and teaching in neuro-evolution. Proceedings 7th Conference on Genetic Algorithms. San Francisco, Cal., Morgan Kaufmann.
SCHOR, J. B. (2004) Born to Buy: The Commercialized Child and the New Consumer Culture. New York: Scribner.
PARISI, D. (1997) Cultural evolution in neural networks. IEEE Expert 12: 9 - 11.
Return to Contents of this issue
© Copyright Journal of Artificial Societies and Social Simulation, [2006]