My Way or the Highway: a More Naturalistic Model of Altruism Tested in an Iterative Prisoners' Dilemma
Journal of Artificial Societies and Social Simulation
vol. 9, no. 2
<https://www.jasss.org/9/2/4.html>
For information about citing this article, click here
Received: 18-Aug-2005 Accepted: 08-Mar-2006 Published: 31-Mar-2006
 Abstract
Abstract

|

|
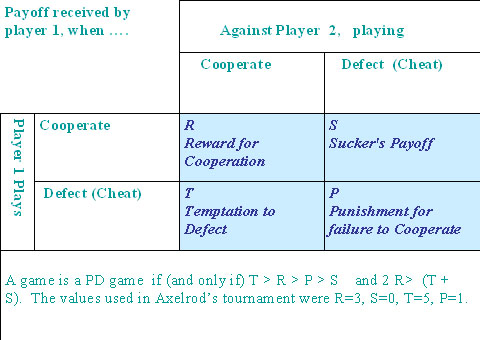
|

|
First Cooperate or First Defect Strategies: Because on the first game of a match, strategies have no information concerning the play of the other strategies, a first round decision must be made unconditionally whether to cooperate or defect.
Conditional or Unconditional Strategies: On the second and subsequent rounds, conditional strategies become possible, that is, strategies that were conditional on the other players' first round move. Some strategies make use of that information and others do not.
Leave-Stay or Cooperate-Defect Strategies: Conditional strategies can be further distinguished on the basis of what they did when their conditions were met.

|
| Figure 1. |

|
| Figure 2. |

|
| Figure 3. |

|
| Figure 4. |
  
|
| Figures 4a, 4b and 4c. |
AXELROD R (1997) The Complexity of Cooperation: Agent-Based Models of Competition and Collaboration. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
AXTELL R, Axelrod R, Epstein J M, and Cohen M D (1996) Aligning simulation models: A case study and results. Computation and Mathematical Organization Theory, 1, 123-141.
BARKER G (1993), "Models of biological change: Implications of three studies of 'Lamarckian' change". In Bateson P P G et al. (Eds.), Perspectives in Ethology, Volume 10: Behavior and Evolution. New York: Plenum Press.
BOONE R T and Macy M W (1999) Unlocking the doors of prisoner's dilemma: Dependence, selectivity, and cooperation. Social Psychology Quarterly, 62, 32-52.
BULLER D J (2005) Adapting Minds. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
COSMIDES L and Tooby J (1992), "Cognitive adaptations for social exchange". In Barkow J H, Cosmides L and Tooby J. (Eds.), The Adapted Mind: Evolutionary Psychology and the Generation of Culture. New York: Oxford.
DE WAAL F (1982) Chimpanzee Politics. New York: Harper & Row, Publishers, Inc.
HIRSCHMAN A (1970) Exit, Voice, and Loyalty. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
LORENZ K (1935/1970), "Companions as factors in the bird's environment". In Lorenz K, (tr. Martin, R) Studies in Animal and Human Behavior, Volume 1. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
MACY M W and Skvoretz J (1998) The evolution of trust and cooperation between strangers: A computational model. American Sociological Review, 63, 638-660.
ORBELL J and Dawes R (1993) Social welfare, cooperator's advantage, and the option of not playing the game. American Sociological Review, 58, 787-800.
SHERRATT T N and Roberts G (1998). The evolution of generosity and choosiness in cooperative exchanges. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 193.
SOBER E and Wilson D S (1999) Unto Others: The Evolution and Psychology of Unselfish Behavior. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
THORNDIKE, E L (1911) Animal Intelligence, experimental studies. New York: Macmillian.
TRIVERS, R (1971/1978) The Evolution of Reciprocal Altruism. Quarterly Review of Biology, 1971. As reprinted in Clutton-Brock T H and Harvey P H (Eds.), Readings in Sociobiology, pp 189-232. New York: WH Freeman.
WILKINSON G S (1984) Reciprocal Food Sharing in the Vampire Bat. Nature, Issue 308. pp. 181-184.
YAMAGISHI T and Hayashi N (1996) Selective play: Social embeddedness of social dilemmas. In Liebrand W and Messic D (Eds.) Frontiers in Social Dilemmas Research, Berlin: Springer.
Return to Contents of this issue
© Copyright Journal of Artificial Societies and Social Simulation, [2006]